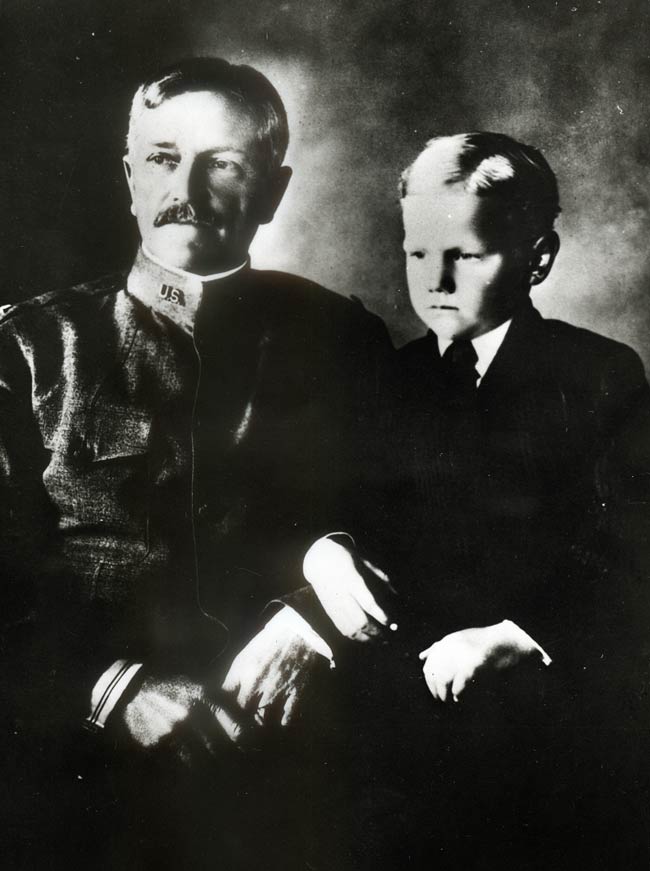
General George Patton by Robert F. Cranston, 1945 color carbro print, from the National Portrait Gallery
General George Patton by Robert F. Cranston, 1945 color carbro print, from the National Portrait Gallery Patton’s first invention, a saber, grew out of his participation in the 1912 Olympic Games. The Army's entry in the first modern pentathlon, Patton was the only American among the 42 pentathletes in Stockholm, Sweden that year. Patton finished fifth overall in the competition that involved pistol firing, swimming, fencing, an equestrian competition, and a footrace. Following the Olympics, Patton traveled through Europe, seeking to learn more about swordsmanship.
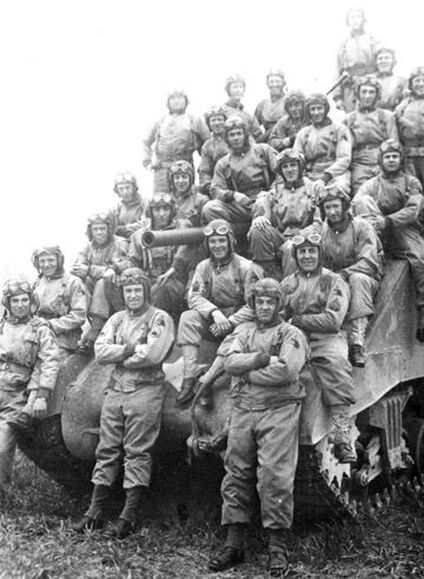
Patton did not rest on his obsolete laurels. During World War I, he became a leading voice in the use of tanks. Immediately after the war, he became involved in improvements in his beloved iron horses. The first, which he worked on between 1919 and 1921, was a new coaxial gun mount that allowed greater range of motion for a tank’s big gun.
 (Photo: 44thcollectorsavenue.com)
(Photo: 44thcollectorsavenue.com)